There are so many reasons you may decide to go on birth control. Whether you want to not get pregnant, stop having your period, or even just try to clear your skin up there are a multitude of options to choose from.
Image via Body+Soul
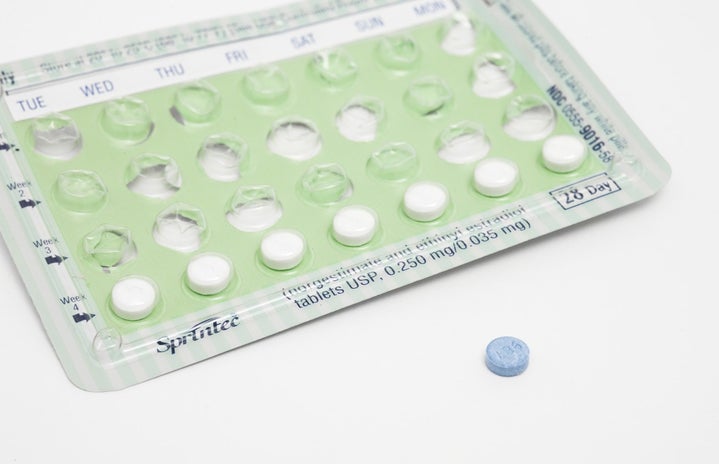
Birth control pill
What it is: Along with casually being called the pill, and more formally oral contraceptive, the birth control pill is a safe, affordable, effective method of birth control. The pill has hormones in it that prevent ovulation, which means that there’s no egg present to be fertilized by sperm. It also thickens cervical mucus to deter sperm. It comes in a pack that’s taken once a day, and is most effective when taken daily. There are two types of combination that is both estrogen and progestin, these are most common, and progestin-only pills. The combination pill you have to take every day, and it’s the progestin-only pills that you have to take within the same three hours every day to stay protected from pregnancy.
Effectiveness: 91%, has to be taken on time every day, less effective if not taken properly.
Cost: $0-50
Pros:
- It can regulate, lessen, and even make you period free
-
It can reduce period cramps
Combination pill only:
-
It can prevent or lessen acne
-
It can prevent or lessen bone thinning
-
It can prevent or lessen cyst in breast and ovaries
-
It can prevent or lessen endometrial and ovarian cancers
-
It can prevent or lessen serious infections in ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus
-
It can prevent or lessen iron deficiency
-
It can prevent or lessen PMS
Cons:
- The first few months may involve headaches, nausea, sore breast, and/or spotting, but these often only last the first few months after starting the pill
-
It does not prevent against STDs
-
You have to take it every day
Image via Women’s Health
Birth control shot
What it is: Also called the depo shot, Depo-Provera, is a convenient method of contraceptive that also allows for a degree of privacy. The depo shot contains the hormone progestin and similar to the pill, prevents ovulation and thickens cervical mucus. You need a new shot every 12-13 weeks, roughly every three months, and this is often performed by a doctor or nurse.
Effectiveness: 94% effective, less effective if you don’t get it in a certain window
Cost: $0-100
Pros:
- You’re able to get it in the privacy of your doctor’s office around four times a year.
-
After a year of use, it can regulate, lessen, and even make you period free.
-
It can prevent from uterine cancer
-
It can prevent an ectopic pregnancy
Cons:
- It’s in the form of an injection
-
You must travel to a doctor’s office or health center every three months for the injection
-
It may cause spotting between periods and longer periods in the first year of use
-
It may cause nausea
-
It may cause weight gain
-
It may cause headaches
-
It may cause breast tenderness
-
It may cause depression
-
It may cause bruising at the injection site
-
It may cause a permanent small skin indent at the injection site
-
It can delay pregnancy for up to 9-10 months after stopping use
-
It doesn’t protect against STDs
Image via SELF
Intrauterine Device (IUD)
What it is: A small device placed within the uterus, an IUD is often a T-shaped plastic or copper intrauterine contraceptive. There are 5 different types of IUDs: Paragard, Mirena, Kyleena, Liletta, and Skyla, and the Paragard is of the copper variety. The copper kind is hormone-free and works because sperm does not like copper, and can’t make it to the egg. The other brands use the hormone progestin to prevent pregnancy which works just like the pill does. The convenient thing about IUDs is how they can last from 3 to 12 years depending on the brand. A copper IUD can also be used as an emergency contraceptive up to 5 days after unprotected sex and is 99.9% effective. Insertion takes about five minutes and may be followed by cramping and pain. It’s advised to take it easy after insertion, but shouldn’t feel any worst than a bad period.
Effectiveness: 99% effective, lasts 3-12 years
Cost: $0-1300
Pros:
-
If you get a hormonal IUD your period may lessen or you’ll be period-free by the end of the year
-
Very convenient in the fact you leave it in, and don’t need to worry until it comes time to replace it
-
It can act as an emergency contraceptive depending on the brand you get
-
It’s a very private method in the fact that you don’t need to take anything, make any trips to get it besides at insertion, or do anything before sex to prevent pregnancy
Cons:
-
Pain when IUD is inserted
-
Cramping a couple of days after the IUD is inserted
-
Spotting in between periods
-
Heavier periods and worst menstrual cramps with the Paragard
-
It doesn’t protect against STDs
Image via Clue
Birth control implant (Nexplanon)
What it is: The implant is a very small thin rod that releases… surprise progestin into the body. The implant is placed under the skin of the upper arm, and often doctors numb the spot before insertion. The implant despite lasting 5 years can be removed at any point.
Effectiveness: 99% effective, lasts up to 5 years
Cost: $0-1300
Pros:
-
Being one of the best to forget about it in forms of birth control, making its maintenance very easy
-
It can regulate, lessen, and even make you period free
-
It’s a very private method in the fact that you don’t need to take anything, make any trips to get it besides at insertion, or do anything before sex to prevent pregnancy
Cons:
-
There may be irregular bleeding in the first 6 to 12 months after insertion
-
It may cause headaches
-
It may cause breast pain
-
It may cause nausea
-
It may cause weight gain
-
It may cause ovarian cysts
-
It may cause bruising at the insertion site
-
An infection may develop where the implant was inserted
-
It doesn’t protect against STDs
Image via American Pregnancy Association
Birth control patch
What it is: Placed on your upper arm, stomach, butt or back a transdermal contraceptive patch is a simple method to prevent pregnancy. Replaced between every one to three weeks, the patch releases the hormones estrogen and progestin which you absorb through your skin. It’s most effective if you change it on the same day, and avoid putting lotions, make-up, or oil on that area. The patch should stay in place when you get it wet, be that through sweating, swimming, or showering.
Effectiveness: 91% effective, replaced weekly
Cost: $0-150
Pros:
-
It can regulate, lessen, and even make you period free.
-
It can reduce period cramps.
-
It can prevent or lessen acne
-
It can prevent or lessen bone thinning
-
It can prevent or lessen cyst in breast and ovaries
-
It can prevent or lessen endometrial and ovarian cancers
-
It can prevent or lessen serious infections in ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus
-
It can prevent or lessen iron deficiency
-
It can prevent or lessen PMS
Cons:
-
It must be changed on time or it won’t be effective.
-
There may be irregular bleeding in the first 2 to 3 months after insertion.
-
It may cause headaches
-
It may cause breast pain
-
It may cause nausea
-
It doesn’t protect against STDs
Image via Insider
Vaginal ring
What it is: The birth control ring, also called NuvaRing, is a flexible ring that fits inside your vagina. It works to prevent pregnancy through a release of hormones much like the other forms of birth control. You insert the ring yourself, after making sure it’s not expired, and are fine to leave it in during sex or any sort of physical activities.
Effectiveness: 91% effective, replaced monthly
Cost: $0-200
Pros:
-
It can regulate, lessen, and even make you period free
-
It can reduce period cramps
-
It can prevent or lessen acne
-
It can prevent or lessen bone thinning
-
It can prevent or lessen cyst in breast and ovaries
-
It can prevent or lessen endometrial and ovarian cancers
-
It can prevent or lessen serious infections in ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus
-
It can prevent or lessen iron deficiency
-
It can prevent or lessen PMS
Cons:
-
There may be irregular bleeding in the first 2 to 3 months after insertion
-
It may cause headaches
-
It may cause breast pain
-
It may cause nausea
-
It does not protect against STDs
Image via Mayoclinc
Diaphragm
What it is: A form of internal contraceptive, a diaphragm is a shallow cup that covers the cervix to prevent the entrance of sperm. It works best when spermicide is applied to the diaphragm, and then it’s inserted similar to a menstrual cup. The spermicide last up to two hours before sex, but the diaphragm needs to stay in place at least six hours after the last time one has sex.
Effectiveness: 92-96% effective, only effective if used with spermicide
Cost: $50-200
Pros:
-
It can fit in your pocket or bag, easy to bring on the go
-
It can be placed up to two hours before sex
-
It is hormone-free
-
It is renewable
Cons:
-
It can be difficult to correctly insert
-
It is only effective when used with spermicide
-
You need to find a size that fits your body
Image via Fairview
Spermicide
What it is: A substance made up of chemicals that are placed inside the vagina to block the entrance of the cervix and stop the movement of sperm. It can be used both by itself and with other forms of birth control, such as a diaphragm. It comes in many forms such as creams, gels, film, foam, and suppositories which is an insert that melts into a cream.
Effectiveness: 72% effective
Cost: $0.60-15
Pros:
-
It’s very cheap in comparison to other forms of birth control
-
It’s over the counter
-
It’s easy to transport
-
It’s hormone-free
Cons:
-
It may irritate sensitive tissue
-
It could increase your risk for STD’s if used multiple times a day
-
It can be very messy
Image via Cosmopolitan
External condom
What it is: This is probably a well-known form of contraceptive for most people. Condoms are a form of external contraceptive that’s worn on the penis during sex. It prevents sperm from entering the vaginas.
Effectiveness: 85% effective, less effective if not used properly, can tear
Cost: $0-2
Pros:
-
External condoms aside from internal condoms are the only form of contraceptive that protects against STDs
-
It’s cheap
-
It’s over the counter
-
It can help other forms of birth control to be more effective
-
It has no side effects
-
It protects against STDs
Cons:
-
Some people are allergic to latex, but there are plastic versions of external condoms.
Image via Youbeauty
Internal condom
What it is: Colloquially known as a “female condom” this is the opposite of the external condom, but it provides all the same drawbacks and benefits.
Effectiveness: 79% effective
Cost: $0-2
Pros:
-
It’s cheap
-
It’s over the counter
-
It can help other forms of birth control to be more effective
-
It has no side effects
-
It protects against STDs
Cons:
-
Some people are allergic to latex, but there are plastic versions of internal condoms